Over 4000 Android Apps Expose Users’ Data via Misconfigured Firebase Databases
More than 4,000 Android apps that use Google’s cloud-hosted Firebase databases are ‘unknowingly’ leaking sensitive information on their users,
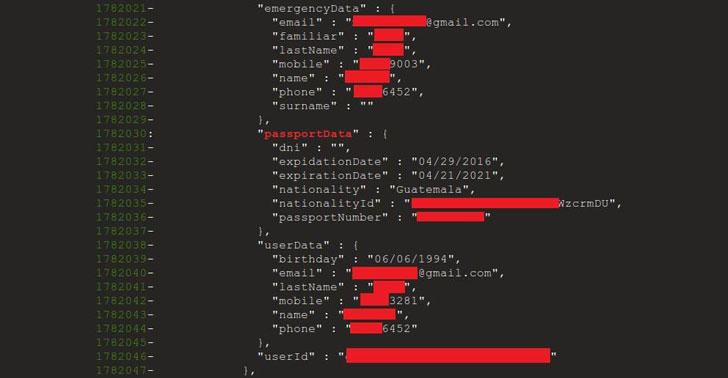
including their email addresses, usernames, passwords, phone numbers, full names, chat messages and location data. Firebase
The investigation, led by Bob Diachenko from Security Discovery in partnership with Comparitech,
is the result of an analysis of 15,735 Android apps, Firebase
which comprise about 18 percent of all apps on Google Play store.
“4.8 percent of mobile apps using Google Firebase to store user data are not properly secured,
allowing anyone to access databases containing users’ personal information, access tokens,
and other data without a password or any other authentication,” Comparitech said.
securely store app data and files, fix issues, and even engage with users via in-app messaging features.
With the vulnerable apps in question Firebase
Given that Firebase is a cross-platform tool, the researchers also warned that the misconfigurations are likely to impact iOS and web apps as well.
The full contents of the database, spanning across 4,282 apps, included:
- Email addresses: 7,000,000+
- Usernames: 4,400,000+
- Passwords: 1,000,000+
- Phone numbers: 5,300,000+
- Full names: 18,300,000+
- Chat messages: 6,800,000+
- GPS data: 6,200,000+
- IP addresses: 156,000+
- Street addresses: 560,000+
Diachenko found the exposed databases using known Firebase’s REST API that’s used to access data stored on unprotected instances,
Aside from 155,066 apps having publicly exposed databases,
Complicating the matter further is the indexing of Firebase database URLs by search engines such as Bing,
After Google was notified of the findings on April 22, the search giant said it’s reaching out to affected developers to patch the issues.
This is not the first time exposed Firebase databases have leaked personal information.
Leaving a database exposed without any authentication is an open invitation for bad actors.
Users, for their part, are urged to stick to only trusted apps and be cautious about the information that’s shared with an application.